Chimpanzees are living simplest in African rainforests and jungles. Orangutans are living simplest within the forests of Indonesia. However people are living nice-looking a lot in every single place. Our species has unfold throughout frozen tundras, settled on mountaintops and known as alternative terminating environments house.
Scientists have traditionally observable this pliability as one of the crucial hallmarks of recent people and an indication of the way a lot our brains had advanced. However a unused find out about hints that perhaps we aren’t so particular.
1,000,000 years in the past, researchers have discovered, an extinct species of human family referred to as Homo erectus thrived in a harsh barren region soil as soon as regarded as off limits prior to Homo sapiens got here alongside.
“It’s a significant shift in the narrative of adaptability, expanding it beyond Homo sapiens to include their earlier relatives,” stated Julio Mercader, an archaeologist on the College of Calgary and an creator of the find out about, which used to be printed Thursday within the magazine Communications Earth and Shape.
Fossils of our early forerunners accumulated over many a long time looked as if it would ascertain the particular adaptability of our species. Our ancestors, referred to as hominins, break off from alternative apes in Africa about six million years in the past and lived for tens of millions of years in obvious jungles. They didn’t appear to are living in terminating environments.
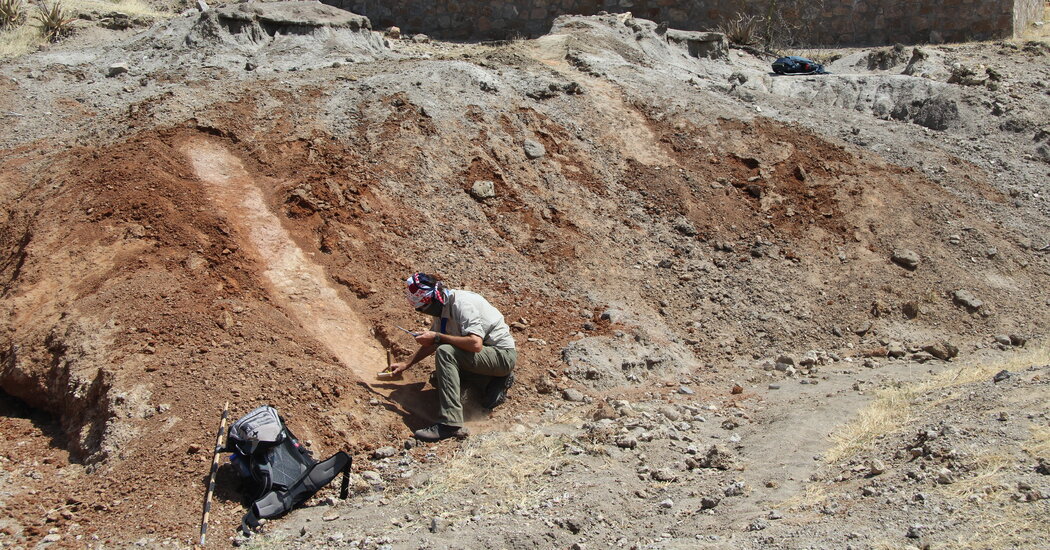
Dr. Mercader and his colleagues intently tested environments in East Africa, which has yielded probably the most richest troves of hominin fossils. They picked a web page in northern Tanzania known as Engaji Nanyor the place paleoanthropologists had up to now discovered fossils of Homo erectus.
Homo erectus is assumed to have advanced about 2 million years in the past in Africa. They had been the primary to achieve the stature of recent people, and so they had lengthy narrow legs to run on. Their brains had been additionally better than the ones of previous hominins, even though simplest about two-thirds the dimensions of our personal.
At some time, Homo erectus expanded out of Africa, getting so far as Indonesia, the place they turned into extinct about 100,000 years in the past. In Africa, many researchers suspect, they gave get up to our personal species within the era a number of hundred thousand years prior to disappearing there as neatly.
Dr. Durkin and his colleagues got down to decide precisely what sort of surrounding Homo erectus lived in 1,000,000 years in the past at Engaji Nanyor. They checked out fossil pollen grains, analyzed the chemistry of the rocks and looked for alternative clues to the soil.
“These studies are an immense amount of work,” stated Elke Zeller, a condition scientist on the College of Arizona who used to be now not concerned within the mission.
For masses of hundreds of years, the researchers motivated, Engaji Nanyor were a comfy obvious jungle. However round 1,000,000 years in the past, the condition parched up and the bushes vanished. The soil grew to become to a Mojave-like barren region shrub land — a particularly arid park that appeared inhospitable for early hominins.
“The data led us to a pivotal question: How did Homo erectus manage to survive and even thrive under such challenging conditions?” Dr. Mercader stated.
In lieu of getaway, the hominins discovered how continue to exist of their converting house. “Their greatest asset was their adaptability,” Dr. Mercader stated.
They modified the way in which they looked for animal carcasses to scavenge, for instance. The hominins discovered the ponds and streams that sprang into life then storms. They didn’t simply drink at those fleeting watering holes. They hunted the animals that still confirmed up there, butchering their carcasses via the hundreds.
The hominins additionally tailored via upgrading their equipment. They took extra offer when chipping flakes from stones to present them a sharper edge. In lieu than simply pick out up rocks anyplace they had been, they most well-liked subject matter from explicit parks. And when they made a device, they carried it with them.
“They may have had strategies where they basically say, ‘This is a good tool. I should bring it with me and be ready if we find food,’” stated Paul Durkin, a geologist on the College of Manitoba who additionally labored at the find out about.
Dr. Durkin and his colleagues discovered that Engaji Nanyor used to be on the southern fringe of a gigantic belt of barren region shrub lands that stretched out of Africa, throughout a lot of the Center East and into Asia. It’s imaginable that the adaptability that Homo erectus displayed at Engaji Nanyor helped them enlarge to alternative continents.
Dr. Zeller and her colleagues have taken a unique way to learning hominins: growing large-scale condition fashions to determine what statuses had been like all the way through our evolution. Their fashions, just like the unused find out about, counsel that Homo erectus can have thrived in environments that had been as soon as concept too harsh for species alternative than our personal.
Research like those Dr. Zeller and the Engaji Nanyor group are carrying out “are all starting to tell the same story,” she stated. “We definitely have to look further back in time to understand our adaptability.”